LTE - Resource Block Flexible Bandwidth
A transmitted OFDMA signal can be carried by a number of parallel
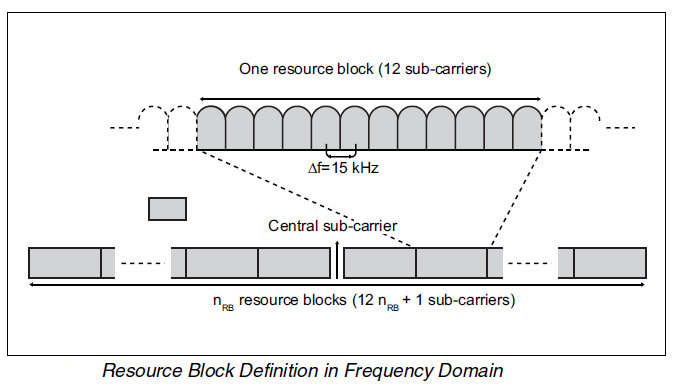
subcarriers. Each LTE subcarrier is 15 kHz. Twelve subcarriers (180 kHz) are
grouped into a resource block. The downlink has an unused central subcarrier. Depending
on the total deployed bandwidth, LTE supports a varying number of resource
blocks.
The following illustration shows resource block definition:
A
resource block is limited in both the frequency and time domains. One resource
block is 12 subcarriers during one slot (0.5 ms).
In
the downlink, the time-frequency plane of OFDMA structure is used to its full
potential. The scheduler can allocate resource blocks anywhere, even non-contiguously.
A variant of OFDMA is used in the uplink. This
variant requires the scheduled bandwidth to be contiguous, forming in effect a
single carrier. The method, called SC-FDMA, can be considered a separate
multiple access method.
A
user is scheduled every Transmission Time Interval (TTI) of 1 ms, indicating a
minimum of two consecutive resource blocks in time at every scheduling instance.
The minimum scheduling in the frequency dimension is 12 subcarriers that is the
width of one resource block in the frequency dimension. The scheduler is free
to schedule users both in the frequency and time domain. Show in Figure as
example of two users scheduled in the time and frequency domain for the
downlink and the uplink:
The
defined LTE bandwidths in 3GPP are the following:
In Table Bandwidths and Resource Blocks Specified in 3GPP
Bandwidth
|
Number of Resource Blocks nRB
|
1.4 MHz
|
6
|
3.0 MHz
|
15
|
5.0 MHz
|
25
|
10.0 MHz
|
50
|
15.0 MHz
|
75
|
20.0 MHz
|
100
|